Background
The current state for instrument approaches to aerodromes in Europe varies from Non Precision Approaches (NPA) (with lateral guidance only) based on ground NAVAIDS or basic GPS, to Precision Approaches (PA) (with lateral and vertical guidance) based on ground ILS or MLS systems. With the introduction of the SBAS systems augmenting the American GPS system (like EGNOS in Europe, WAAS in USA, MSAS in Japan or GAGAN in India), it has been possible to introduce new approaches, whose performance is between PAs and NPAs. These approaches with vertical guidance, called LPV/APV, provide the means to perform approaches with a performance close to the PA, but with no need of ground infrastructure.
Objectives
The project objectives are: to accelerate the development, certification, installation and marketing of EGNOS-enabled avionics; to design, develop and publish details of EGNOS LPV approach procedures at airports throughout Europe. With the airline partners, an initial set of candidate airports has been identified, with a view to advantageous use of the LPV procedures for their operation; to commission aircraft into operation that are equipped and certified with the required avionics, with not only the EGNOS receiver but also the updated Flight Management System, which is the key avionics element to provide the aircraft with the capability to perform LPV approaches; to develop customised business cases for the partner airlines and end users by analysing real-life costs and benefits of using EGNOS; to promote the adoption of EGNOS in general/business aviation and regional airlines by the dissemination and awareness of the results and benefits to these communities through the various associations; to identify operational practices that will lead to a successful EGNOS adoption, knowledge building and dissemination to a Europe-wide network of aviation community members with a strong interest in GNSS technology, focusing on showing economic and operational benefits to end users.
Description
The overall project concept is the acceleration of the EGNOS adoption in the aviation sector. Not only the EGNOS receivers but the complete required avionics suite will be installed in the fleet of the regional airlines and corporate users, partners of the ACCEPTA proposal and other potential newcomers during the project lifetime. There will be a wide-scale real-life adoption of the EGNOS-enabled LPV approaches throughout European airports where the SBAS signal is available and certified, focusing on the Topic’s first objective of the Call (acceleration of the development, certification, installation and marketing of EGNOS enabled avionics). The project will operationally introduce the EGNOS aviation applications in the most promising key niche markets that are interested in the use of EGNOS, namely regional airlines and corporate aviation. It takes into account the results of previous studies for the introduction of the EGNOS-enabled operations to the end users, but this is not a continuation of past projects, so there are no more pre-operational flight demonstrations, no more single demonstrations with only one aircraft test (specially modified for the test) and a single airport. It will closely collaborate with SESAR, and other FP7 and EUROCONTROL-related projects in order not to duplicate activities and thus make better use of available public funds.
Results
ACCEPTA will provide a full-scale real-life operational context for the adoption and use of the EGNOS signal as a key positioning and navigation sensor that will produce valuable insights and economic data to drive the progress of GNSS programmes in Europe. The ‘business’ aspects of application of EGNOS-based LPV procedures will be the predominant area of research in this project. Also the validity of the EGNOS signal in space in support of these operations will be verified, to establish evidence of the business arguments of the airline and to assure that operations can indeed be executed. Other impacts are: reduced operating costs: reduced costs associated with CA in terms of missed approaches, diversion of flights to alternate airports, etc.; less expensive onboard avionics equipment; elimination of ground NAVAIDS infrastructure; enhanced efficiency of aircraft operator operations, specifically flight operations; reduced operational costs, especially during the approach phase; optimised use of all resources for all involved partners; improved punctuality (on time performance) and reduced delays; greater flexibility in the planning and management of the flights. Dissemination will be through the European Business Aviation Association (EBAA) and European Regional Airlines Association (ERAA), members of the ACCEPTA consortium.
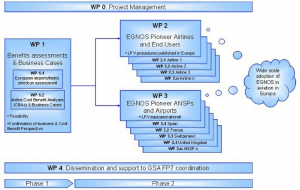
ACCEPTA Work Breakdown Structure
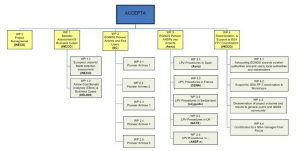
ACCEPTA Interdependencies of WPs